Google Chrome Adoption
So I obviously don't need to tell you what Chrome is, even if it is a little over-hyped. I found this interesting thou Google Chrome Adoption Stats from BlogoWogo. It's plain to see that this could prove to be a key strategic move in the history of Google, especially when you consider the number of people now using all of Google's Javascript intensive online applications.
If you're bored, check out the Gmail performance difference between Chrome (or even Firefox) and Internet Explorer.
7 Habits for Effective Text Editing
It's goes without saying - Vim kicks ass. As my editor of choice I found this video quite informative:
The following video will give an overview of the large number of ways of using Vim in a smart way to edit programs, structured text and documentation. Examples will be used to make clear how learning a limited number of habits will avoid wasting time and lower the number of mistakes.
This video is presented by Bram Moolenaar, whom is mostly known for being the benevolent dictator (and author) of the text editor Vim. He also did the A-A-P project in between Vim version 6.0 and 7.0. Now he works for Google in Zurich, still improving Vim on the side.
Idiot of the Year - Bicycle Stunt Goes Wrong
FreeBSD - Installation and Migration to a New SATA Harddisk
My old dual 300GB ATA mirrored disks were becoming full and the pains of having low disk space were becoming too much of a strain, it was time to get some bigger disks...
This article explains the procedures required in FreeBSD to install and partition the new disks as well as migrating the data from the older disks using RSYNC.
My current configuration:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Capacity Mounted on /dev/ad8s1c 3.0G 290M 2.5G 10% / devfs 1.0K 1.0K 0B 100% /dev /dev/ad8s3c 446G 405G 5.7G 99% /usr procfs 4.0K 4.0K 0B 100% /proc /dev/ad10.eli 458G 412G 9.6G 98% /mnt/backup /dev/ad0.eli 275G 252G 895M 100% /mnt/300gb_primary /dev/ad1.eli 275G 228G 25G 90% /mnt/300gb_backup
Unfortunately the two 300GB drives are ATA which is now an old technology, since I was taking a plunge I may aswell move to something better while I'm making the change at all.
Required Hardware
A quick look on Komplett (whom I whole heartedly recommend) and 2 x Samsung spinpoint 500GB SATA disks were purchased on special for only €144.

Two SATA cables (i just had these lying around):
And a SATA interface, or in my case a Sunsway/ST Lab PCI SATA interface because the existing 500GB's are already using up the motherboard's SATA slots.
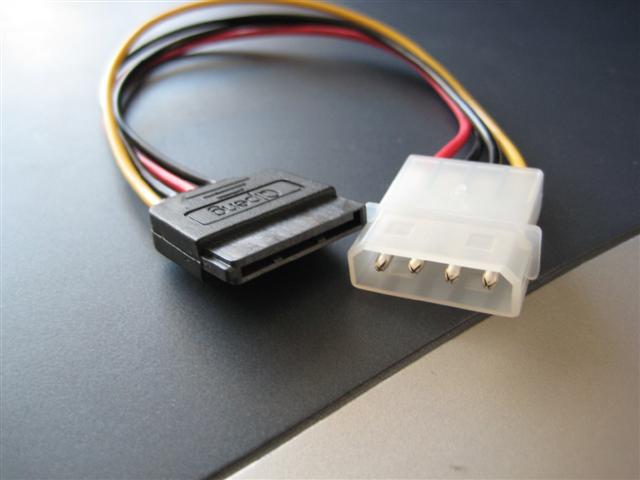
Unfortunately I didn't fully investigate what was required and upon inspection I discovered I needed more SATA power connectors since the two existing connectors were being used, as a result the following little gadget was purchased from maplin:

Installation Procedure
The SATA PCI card was installed, the two disks attached to it via the SATA cables and the drives were powered by connecting them to the PSU via the SATA power adapters. The adapters I got from maplin had poor quality PSU connectors on them (the white ones) where the pins could move.. this made it painful to connect up since all 4 pins had to be aligned before the connector properly fit.
Everything was switched on and FreeBSD began its bootup, all drives were successfully detected as can be seen on the dmesg output:
ad0: 286168MB <WDC WD3000JB-00KFA0 08.05J08> at ata0-master UDMA100 ad1: 286168MB <WDC WD3000JB-00KFA0 08.05J08> at ata0-slave UDMA100 ad4: 476940MB <SAMSUNG HD501LJ CR100-12> at ata2-master SATA150 ad6: 476940MB <SAMSUNG HD501LJ CR100-12> at ata3-master SATA150 ad8: 476940MB <SAMSUNG HD501LJ CR100-10> at ata4-master SATA150 ad10: 476940MB <SAMSUNG HD501LJ CR100-10> at ata5-master SATA150
I use an encrypted disk configuration using GELI and so before we can use FDISK to partition the drives we must initialize disk encryption, at this point I should point out that for more details on configuring disk encryption on FreeBSD see encrypting file system partitions in FreeBSD article.
Firstly, we initialize disk encryption on the devices. Since I'm already using disk encryption we're going to use my old key for initializing the encryption. This is the same keyfile I use for all my drives:
[root@orion] (/etc): geli init -s 4096 -K /root/.geli_keys/ad1.key /dev/ad4 Enter new passphrase: Reenter new passphrase: [root@orion] (/etc): geli attach -k /root/.geli_keys/ad1.key /dev/ad4 Enter passphrase: [root@orion] (/etc): tail -3 /var/log/messages Apr 12 11:56:21 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Device ad4.eli created. Apr 12 11:56:21 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Encryption: AES-CBC 128 Apr 12 11:56:21 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Crypto: software
The same procedure is repeated for the ad6 disk.
When that's done we newfs the entire disks (for my needs I prefer to have one enormous slice):
[root@orion] (/etc): newfs /dev/ad4.eli > /ad4_superblocks.txt [root@orion] (/etc): newfs /dev/ad6.eli > /ad6_superblocks.txt
Note that I have redirected the newfs output to a text file since the superblock locations can be useful for disaster recovery.
Then, I enable softupdates:
[root@orion] (/etc): tunefs -n enable /dev/ad4.eli tunefs: soft updates set [root@orion] (/etc): tunefs -n enable /dev/ad6.eli tunefs: soft updates set
Now we need to mount these disks, so we create appropriately named mount points:
[root@orion] (/etc): mkdir /mnt/{500gb_primary,500gb_backup}
And now our /etc/fstab entries:
# New 500GB SATA disks /dev/ad4.eli /mnt/500gb_primary ufs rw 0 0 /dev/ad6.eli /mnt/500gb_backup ufs rw,noauto 0 0
Next we mount the drives at our mountpoints:
[root@orion] (/etc): mount /mnt/500gb_primary/ [root@orion] (/etc): mount /mnt/500gb_backup/
And just to confirm that we're looking good:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Capacity Mounted on /dev/ad8s1a 3.0G 290M 2.5G 10% / devfs 1.0K 1.0K 0B 100% /dev /dev/ad8s3c 446G 405G 5.7G 99% /usr procfs 4.0K 4.0K 0B 100% /proc /dev/ad10.eli 458G 412G 9.6G 98% /mnt/backup /dev/ad0.eli 275G 252G 895M 100% /mnt/300gb_primary /dev/ad1.eli 275G 228G 25G 90% /mnt/300gb_backup /dev/ad4.eli 458G 8.0K 422G 0% /mnt/500gb_primary /dev/ad6.eli 458G 8.0K 422G 0% /mnt/500gb_backup
Yes, truly blissful.
Anyway, the disks are now ready for use, let's migrate over all the data using RSYNC:
[root@orion] (/etc): rsync -av --progress /mnt/300gb_primary/ /mnt/500gb_primary/
For laughs this small little tcsh script helps keep an eye on the overall progress:
[jbw@orion] (~): while (1) while? clear; df -h | grep ad4 while? sleep 1 while? end /dev/ad4.eli 458G 2.9G 419G 1% /mnt/500gb_primary
Now it's coffee time since this has to copy 300GB of data so it's gonna take a little while....
Textbuddy Download Link Is Working Again!
Thanks to David Costello for reporting that the textbuddy download link was dead. It's back up and running now again - sorry about that!
Do It, DO IT!
Snowboarding Trip at Obergurgl in Austria, 2008
Known as the 'gem at high altitude', Obergurgl in Austria is the highest parish in the country . Here's some photos from the xmas 2008 snowboarding trip.



A Troubled Skier

29th Dec 2007 to 3rd Jan 2008 - 1 week, gone in a flash. Oh well, see you next year!
Encrypting File System Partitions in FreeBSD
I've lost a lot of data in the past and learning from these mistakes my current system is setup with a mirrored disk configuration. I have two 500GB disks (sata) and two 300GB disks (ide). On a weekly basis I use rsync to backup the primary drives to their secondary mirrors. This way I can ensure that I always have dual copies of all my important data. For multiple reasons I now wish to encrypt this data so that in the event of someone gaining physical access to this machine they would not be able to read the data if they didn't have the correct passphrase.
Firstly, let's take a look at the relevant bits from /etc/fstab
[root@orion] (~): grep 300 /etc/fstab /dev/ad0s1 /mnt/300gb_primary ufs rw 0 0 /dev/ad1s1d /mnt/300gb_backup ufs rw,noauto 0 0
My plan was to experiment with the filesystem encryption on the secondary disk first. If that proved successful I could then copy all the contents from the primary to the newly encrypted secondary and then move on to making the primary encrypted aswell. Since I'm running FreeBSD 6 I opted to use the newer GELI encryption system - for the sake of getting jumping into experimentation immediately I opted to just use the kernel modules rather than compile support for GELI into the kernel so let's begin:
[root@orion] (~): kldload geom_eli [root@orion] (~): echo 'geom_eli_load="YES"' >> /boot/loader.conf
This loads the geli module into the kernel and the second line ensures that it's automatically loaded upon boot. Next we create our master key, initialize geli on the ad1 disk and finally attach the geli provider:
[root@orion] (~): dd if=/dev/random of=/root/.geli_keys/ad1.key bs=64 count=1 1+0 records in 1+0 records out 64 bytes transferred in 0.000059 secs (1082401 bytes/sec) [root@orion] (~): geli init -s 4096 -K /root/.geli_keys/ad1.key /dev/ad1 Enter new passphrase: Reenter new passphrase: [root@orion] (~): geli attach -k /root/.geli_keys/ad1.key /dev/ad1 Enter passphrase:
Success, as confirmed by /var/log/messages:
Oct 28 13:09:06 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Device ad1.eli created. Oct 28 13:09:06 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Encryption: AES-CBC 128 Oct 28 13:09:06 orion kernel: GEOM_ELI: Crypto: software
With the geli provider attached to the ad1 device we can now work with the disk as normal via the ad1.eli device and geli will transparently handle all the encryption so now we confirm the existance of the geli device and then newfs the encrypted disk:
[root@orion] (~): ls /dev/ad1*
/dev/ad1 /dev/ad1.eli
[root@orion] (~): newfs /dev/ad1.eli
/dev/ad1.eli: 286168.1MB (586072360 sectors) block size 16384, fragment size 4096
using 850 cylinder groups of 336.98MB, 21567 blks, 21568 inodes.
super-block backups (for fsck -b #) at:
160, 690304, 1380448, 2070592, 2760736, 3450880, 4141024, 4831168, 5521312, 6211456,
6901600, 7591744, 8281888, 8972032, 9662176, 10352320, 11042464... etc. etc.
Next it's time to modify our fstab so it's looking at ad1.eli instead of ad1s1d :
[root@orion] (~): sed -i .bak -e 's/ad1s1d/ad1.eli/' /etc/fstab [root@orion] (~): grep 300 /etc/fstab /dev/ad0s1 /mnt/300gb_primary ufs rw 0 0 /dev/ad1.eli /mnt/300gb_backup ufs rw,noauto 0 0 [root@orion] (~): mount /mnt/300gb_backup/
There you have it - surprisingly easy.. and surprisingly powerful. Out of curiousity I decided to do a quick performance test:
[root@orion] (~): dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/300gb_backup/test.img count=10000 bs=1024 10000+0 records in 10000+0 records out 10240000 bytes transferred in 0.387872 secs (26400463 bytes/sec) [root@orion] (~): dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/300gb_primary/test.img count=10000 bs=1024 10000+0 records in 10000+0 records out 10240000 bytes transferred in 0.158931 secs (64430469 bytes/sec)
So it's a little slower than I expected but still, I can live with that for the benefits it provides.
To ensure the drive is mounted upon boot I needed to add the following to my /etc/rc.conf:
geli_devices="ad1" geli_ad1_flags=" -k /root/.geli_keys/ad1.key"
Now it's time to copy the data from the primary disk to this encrypted disk and repeat this process for the primary disk and I'm all done!
Here Comes Another Bubble - Bubble 2.0
With all the hype around Facebook and completely overblown valuations on tech companies I really think this video hits the nail on the head:
Here comes another bubble, indeed.